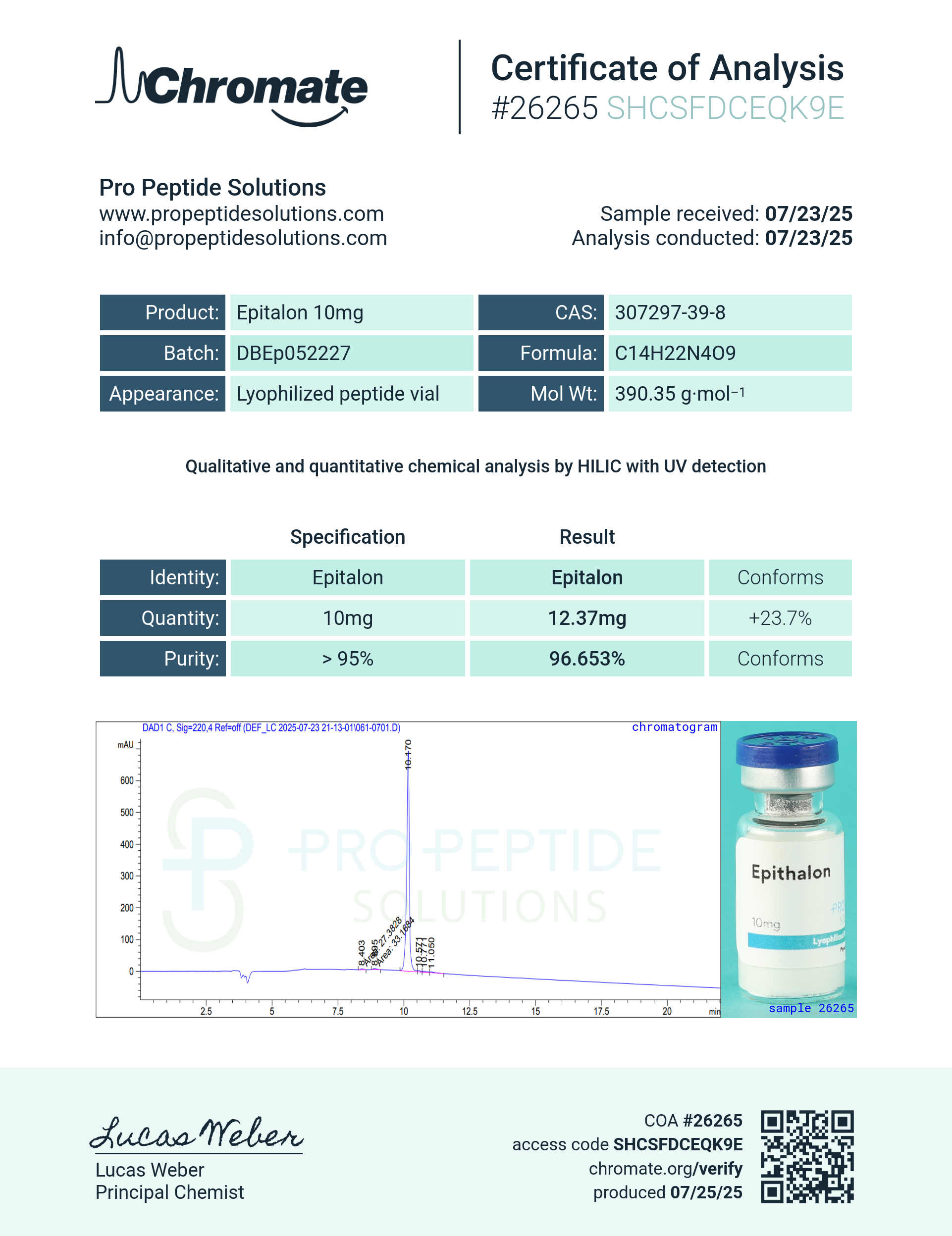
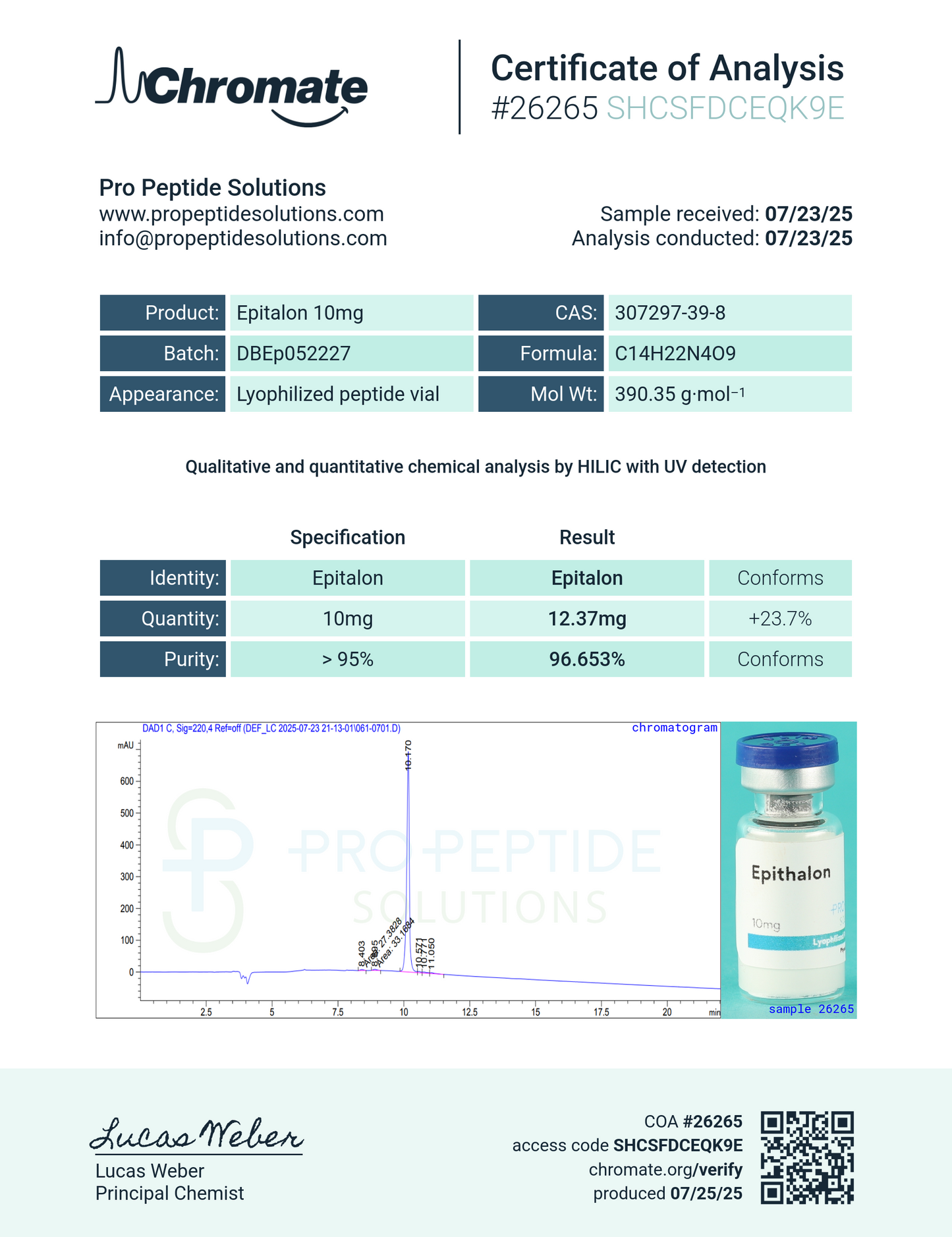
Epithalon (10mg)
Epithalon (10mg)
Epithalon (10mg)


What is Epithalon?
Epithalon—also known as Epitalon, Epithalone, or AEDG peptide—is a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the pineal gland polypeptide epithalamin. First developed in Russia during the 1980s by Professor Vladimir Khavinson’s team, it is comprised of the amino acids alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It is studied for its role in cell cycle regulation, telomerase activation, and longevity mechanisms in preclinical and limited clinical settings.

Chemical Structure of Epithalon
Epithalon is a tetrapeptide with the sequence Ala–Glu–Asp–Gly, a molecular formula of C₁₄H₂₂N₄O₉, and a molecular weight of approximately 390.35 Da. Most studies utilize the canonical α-bonded form of the peptide, available in both free-base and acetate salt forms, as confirmed by PubChem and international peptide databases.
What Are the Effects of Epithalon?
- Telomerase Activation & Telomere Support: In vitro research demonstrates that Epithalon activates telomerase, extending the proliferative lifespan of human somatic cells and exceeding the typical Hayflick limit.
- Longevity and Anti-Aging Effects: In mouse, rat, and Drosophila models, Epithalon reduces mortality rates and extends lifespan through genomic stabilization and antioxidant effects.
- Antioxidant and DNA Integrity: Epithalon has been shown to increase glutathione peroxidase activity and reduce DNA damage and chromosomal aberrations in accelerated-aging animal studies.
- Oncostatic Activity: Animal studies suggest that Epithalon can suppress spontaneous tumors such as mammary gland cancers, possibly by regulating telomerase activity and oncogene expression.
- Pineal/Glandular Signaling & Melatonin Regulation: Research involving elderly rodents and primates has observed normalization of melatonin levels and circadian rhythm markers, including cortisol, following Epithalon administration.